新冠病毒肺炎患者接受静脉-静脉体外膜肺氧合治疗时使用阿加曲班抗凝的活化部分凝血活酶时间及抗IIa监测
Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time and Anti-IIa Monitoring in Argatroban Anticoagulation in COVID-19 Patients on Venovenous Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation.
作者信息
Burša Filip, Frelich Michal, Sklienka Peter, Němcová Simona, Kučerová Zuzana, Jor Ondřej, Romanová Tereza, Kondé Adéla, Janošek Jaroslav, Sagan Jiří, Máca Jan
机构信息
Institute of Physiology and Pathophysiology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Ostrava, Syllabova 19, 703 00 Ostrava, Czech Republic.
Department of Anaesthetics, Resuscitation and Intensive Care Medicine, University Hospital Ostrava, 17. listopadu 1790, 708 00 Ostrava, Czech Republic.
出版信息
Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2025 Jan-Dec;31:10760296251341315. doi: 10.1177/10760296251341315. Epub 2025 May 21.
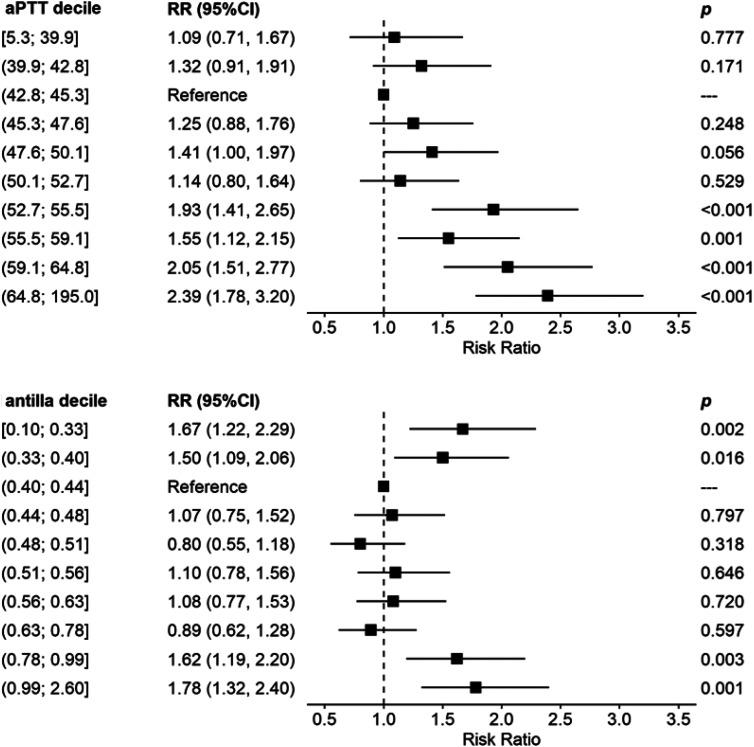
Unfractionated heparin has long been considered the standard anticoagulation in ECMO, despite some pitfalls such as heparin resistance, heparin induced thrombocytopenia (HIT), etc Recently, some centres started to increasingly use argatroban for this purpose, typically using activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) for its monitoring. Direct monitoring of the efficacy of argatroban using Anti-IIa is not yet an established method, although it might be more appropriate as it targets the same pathway.An observational study was performed in adult veno-venous ECMO patients hospitalized with SARS-CoV-2 infection anticoagulated with argatroban to an aPTT target of 40-60 s and Anti-IIa target of 0.4-0.6 µg/mL. Bleeding and thrombotic complications were monitored.Forty-four VV ECMO patients were included, with an overall hospital mortality of approx. 50%. No life-threatening thrombotic events were recorded. The risk of bleeding complications significantly increased with aPTT above 52.7 s and with Anti-IIa values over 0.78 µg/mL. Using the above cut-offs for both the aPTT and Anti-IIa and their combination, the negative predictive value for bleeding was approximately 90%.It seems that the generally recommended limits for Anti-IIa of 1.5 µg/mL may be high. However, further data are needed to confirm lower limits.Trial Registration:retrospectively registered in ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT06038682.
普通肝素长期以来一直被视为体外膜肺氧合(ECMO)中的标准抗凝剂,尽管存在一些缺陷,如肝素抵抗、肝素诱导的血小板减少症(HIT)等。最近,一些中心开始越来越多地将阿加曲班用于此目的,通常使用活化部分凝血活酶时间(aPTT)进行监测。尽管使用抗凝血酶IIa(Anti-IIa)直接监测阿加曲班的疗效可能更合适,因为它针对的是相同的途径,但这尚未成为一种既定方法。对因感染严重急性呼吸综合征冠状病毒2(SARS-CoV-2)而住院并接受阿加曲班抗凝治疗的成年静脉-静脉ECMO患者进行了一项观察性研究,使aPTT目标值达到40-60秒,Anti-IIa目标值达到0.4-0.6μg/mL。监测出血和血栓形成并发症。纳入了44例静脉-静脉ECMO患者,总体医院死亡率约为50%。未记录到危及生命的血栓形成事件。当aPTT高于52.7秒且Anti-IIa值超过0.78μg/mL时,出血并发症的风险显著增加。使用上述aPTT和Anti-IIa的临界值及其组合,出血的阴性预测值约为90%。似乎普遍推荐的Anti-IIa上限1.5μg/mL可能偏高。然而,需要进一步的数据来确认更低的限值。试验注册:在ClinicalTrials.gov上进行回顾性注册,NCT06038682。